SEELab3: PID Controller
| Links:
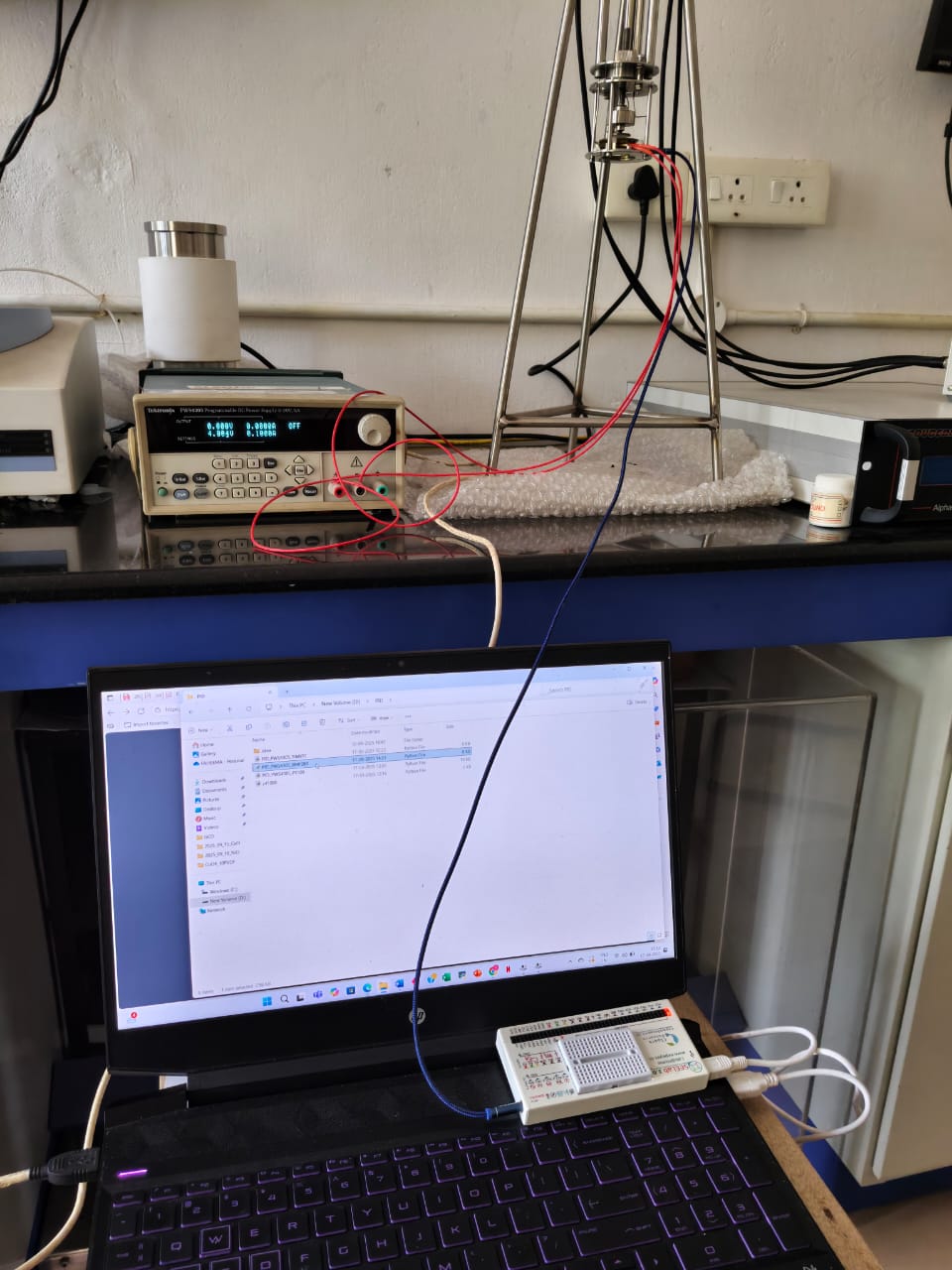
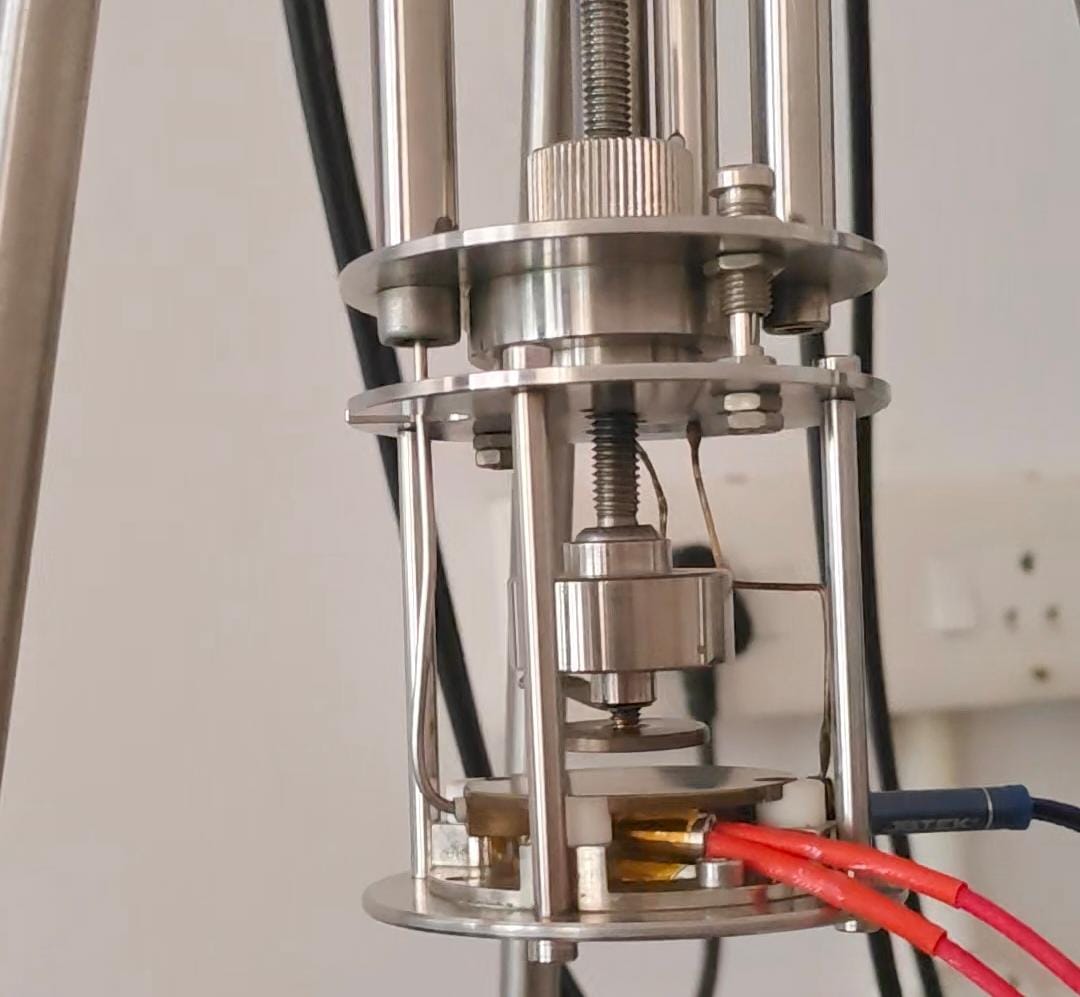
The setup used a BMP280 connected to a SEELab3 for temperature reading, and a heating cartridge whose current is adjusted with a power supply. The algorithm is written in Python with a PyQt5 graphical interface. All measurements and tuning work was carried out by Faheema at Dr. Shahin’s Lab.
Wrote code for a PID controller for a temperature controller dielectric spectroscopy setup. Most commercially available PID controllers use PWM (switching and varying the duty cycle) to adjust heating current, and the transient current spikes completely destroy any readings made near the heater. Therefore, I went with a Tektronix power supply with a USBTMC interface.
The python-usbtmc is quite easy to use on Linux. On windows it is a pain to install drivers, but finally got it running with Zadig. The eyes17lib python library is used to interface with SEELab3.
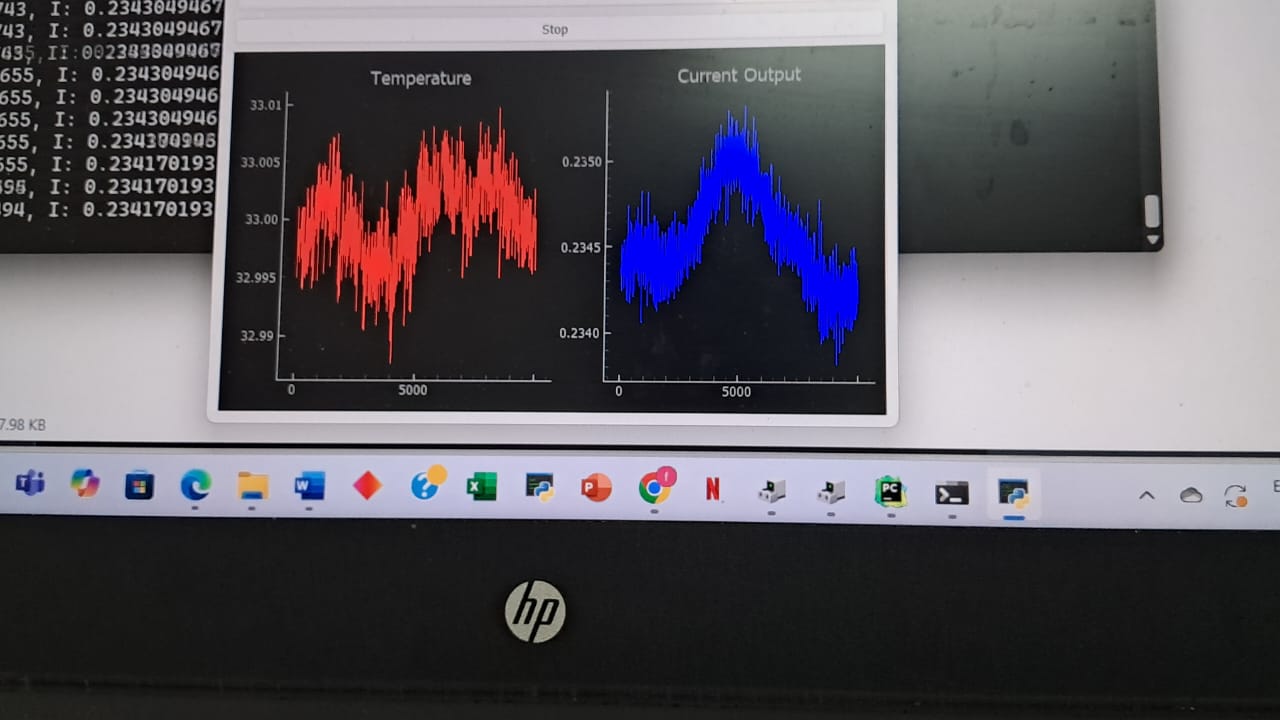
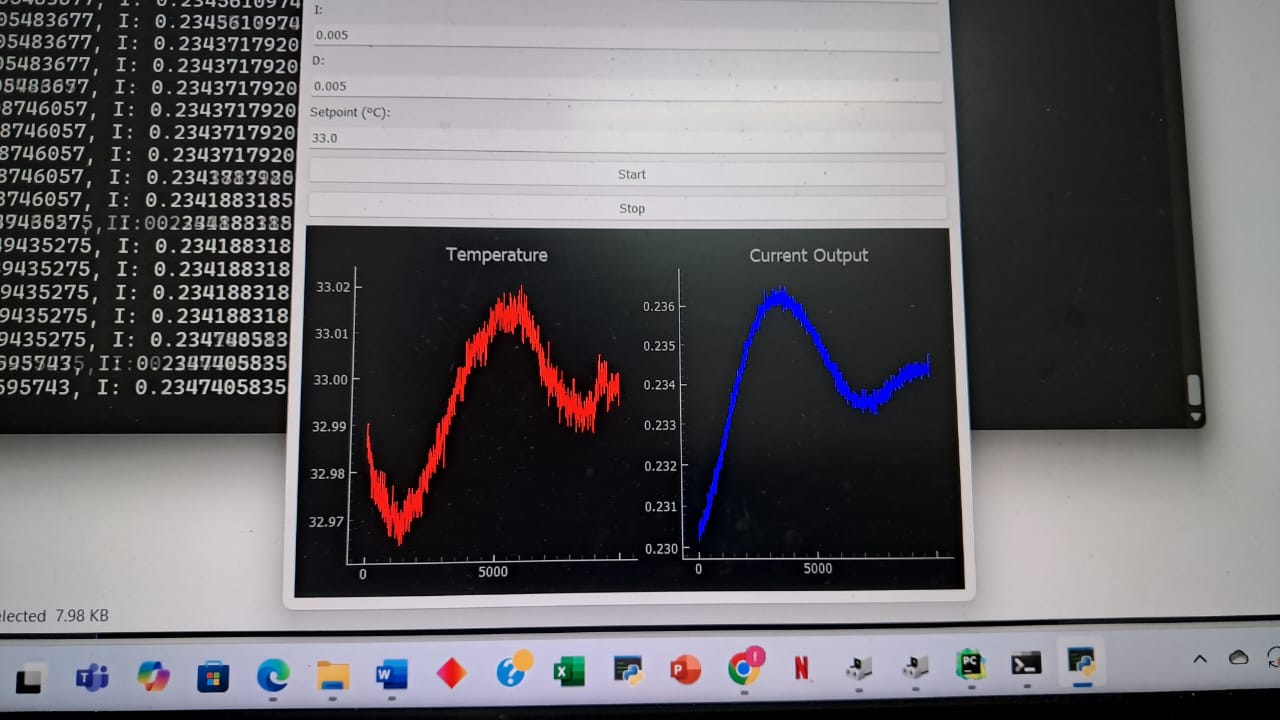
Since the BMP280 has a leat count of 0.01 , the algorithm managed a ridiculous stability of 0.02C

Udev rules
# Keysight Power Supply (0x0699:0x0392)
SUBSYSTEMS=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="0699", ATTRS{idProduct}=="0392", MODE="0666", GROUP="usbtmc", TAG+="usbtmc"
# newer supply from Keysight Technologies, Inc. E36155A
# USB ID: 2a8d:5902
SUBSYSTEMS=="usb", ATTRS{idVendor}=="2a8d", ATTRS{idProduct}=="5902", MODE="0666", GROUP="usbtmc", TAG+="usbtmc"
sudo udevadm control --reload-rules
The Code
'''
PID controller. Connect BMP280
PWS4305 linear power supply.
https://download.tek.com/manual/077048102web.pdf
Remote operation
:SYST:REM
:SYST:LOC
Measurement commands
CURR?
:MEAS:CURR?
:MEAS:VOLT?
Setting commands
CURR x
'''
import sys
import threading
import time, usbtmc
from PyQt5 import QtWidgets, QtCore
import pyqtgraph as pg
import eyes17.eyes
from eyes17 import SENSORS
import numpy as np
from simple_pid import PID
class Expt(QtWidgets.QMainWindow):
update_plots_signal = QtCore.pyqtSignal(float, float) # Signal to update plots
setpoint_changed_signal = QtCore.pyqtSignal(float) # Signal for setpoint changes
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setpoint = 50.0 # Default setpoint
self.pid = None
self.p = eyes17.eyes.open()
self.bmp = SENSORS.BMP280.connect(self.p.I2C)
self.scpi = usbtmc.Instrument(0x0699, 0x0392) # (0x2a8d, 0x5902) for E36155A, (0x0699, 0x0392) for PWS4305 linear
# Get the instrument identification string
idn_string = self.scpi.ask('*IDN?')
print(idn_string)
self.scpi.write('SYST:REM')
self.running = True
self.temperature_data = []
self.current_data = []
self.initUI()
# Set the window title with the instrument ID
self.setWindowTitle(f'PID Temperature Controller - {idn_string}')
# Connect signals to slots
self.update_plots_signal.connect(self.update_plots)
self.setpoint_changed_signal.connect(self.update_setpoint)
def initUI(self):
self.setWindowTitle('PID Temperature Controller')
# Create text fields for initial vaue parameters
self.initial_input = QtWidgets.QLineEdit(self)
self.initial_input.setText('1.04')
# Create text fields for PID parameters
self.p_input = QtWidgets.QLineEdit(self)
self.p_input.setText('0.002')
self.i_input = QtWidgets.QLineEdit(self)
self.i_input.setText('0.005')
self.d_input = QtWidgets.QLineEdit(self)
self.d_input.setText('0.005')
# Create text field for setpoint
self.setpoint_input = QtWidgets.QLineEdit(self)
self.setpoint_input.setText(str(self.setpoint))
self.setpoint_input.editingFinished.connect(self.on_setpoint_changed)
# Create buttons to start and stop the PID loop
self.start_button = QtWidgets.QPushButton('Start', self)
self.start_button.clicked.connect(self.start_pid)
self.stop_button = QtWidgets.QPushButton('Stop', self)
self.stop_button.clicked.connect(self.stop_pid)
# Set up the layout
layout = QtWidgets.QVBoxLayout()
layout.addWidget(QtWidgets.QLabel('initial:'))
layout.addWidget(self.initial_input)
layout.addWidget(QtWidgets.QLabel('P:'))
layout.addWidget(self.p_input)
layout.addWidget(QtWidgets.QLabel('I:'))
layout.addWidget(self.i_input)
layout.addWidget(QtWidgets.QLabel('D:'))
layout.addWidget(self.d_input)
layout.addWidget(QtWidgets.QLabel('Setpoint (°C):'))
layout.addWidget(self.setpoint_input)
layout.addWidget(self.start_button)
layout.addWidget(self.stop_button)
# Create a widget for the plots
self.plot_widget = pg.GraphicsLayoutWidget()
layout.addWidget(self.plot_widget)
# Set up the plots
self.temp_plot = self.plot_widget.addPlot(title="Temperature")
self.current_plot = self.plot_widget.addPlot(title="Current Output")
# Set the central widget
central_widget = QtWidgets.QWidget()
central_widget.setLayout(layout)
self.setCentralWidget(central_widget)
self.pid_thread = threading.Thread(target=self.run_pid)
self.pid_thread.start()
def on_setpoint_changed(self):
new_setpoint = float(self.setpoint_input.text())
self.setpoint_changed_signal.emit(new_setpoint)
@QtCore.pyqtSlot(float)
def update_setpoint(self, new_setpoint):
self.setpoint = new_setpoint
if self.pid is not None:
self.pid.setpoint = new_setpoint
def start_pid(self):
initval = float(self.initial_input.text())
Kp = float(self.p_input.text())
Ki = float(self.i_input.text())
Kd = float(self.d_input.text())
self.setpoint = float(self.setpoint_input.text())
self.pid.tunings = (Kp, Ki, Kd)
self.pid.setpoint = self.setpoint
self.scpi.write('OUTP ON')
#self.pid.auto_mode = True
self.pid.set_auto_mode(True, last_output=initval)
def stop_pid(self):
self.pid.auto_mode = False
self.scpi.write('OUTP OFF')
def kill_pid(self):
self.running = False
if self.pid_thread.is_alive():
self.pid_thread.join()
def run_pid(self):
# PID parameters
Kp = float(self.p_input.text())
Ki = float(self.i_input.text())
Kd = float(self.d_input.text())
self.setpoint = float(self.setpoint_input.text())
self.pid = PID(Kp, Ki, Kd, setpoint = self.setpoint)
self.pid.output_limits = (0, 5) #0 to 5Amps
self.pid.auto_mode = False
self.pid.sample_time = 0.1 # Update every n seconds
while self.running:
temperature = np.average([self.bmp.getVals()[1] for a in range(10)])
# Set the current output
current_output = self.pid(temperature)
# Print debug information
print(f"SET:{self.setpoint}, T: {temperature}, I: {current_output} | {self.pid.auto_mode}")
# Emit signal to update plots
if not self.pid.auto_mode:
current_output = 0
self.update_plots_signal.emit(temperature, current_output)
time.sleep(0.005) # Adjust sleep time as needed
def calculate_temperature(self, resistance):
# Callendar-Van Dusen Constants for standard PT100 (IEC 60751)
A = 3.9083e-3
B = -5.775e-7
C = -4.183e-12 # Used only for T < 0°C
r0 = 98.4
# Approximate temperature using the linear formula
approx_temp = (resistance - r0) / (A * r0)
# Solve Callendar-Van Dusen equation for better accuracy
import math
if resistance >= r0:
# Quadratic formula (valid for T ≥ 0°C)
temp = (-A + math.sqrt(A**2 - 4 * B * (1 - resistance / r0))) / (2 * B)
else:
# For T < 0°C, numerical solving is required due to the cubic term
from scipy.optimize import fsolve
def cvd_equation(T):
return r0 * (1 + A*T + B*T**2 + C*(T - 100)*T**3) - resistance
temp = fsolve(cvd_equation, approx_temp)[0] # Use approx_temp as initial guess
print(f"R:{resistance} , T:{temp}")
return temp
#return temperature
@QtCore.pyqtSlot(float, float)
def update_plots(self, temperature, current_output):
# Limit data arrays to 10,000 points
MAX_POINTS = 10000
self.temperature_data.append(temperature)
self.current_data.append(current_output)
# Keep only the last MAX_POINTS
if len(self.temperature_data) > MAX_POINTS:
self.temperature_data = self.temperature_data[-MAX_POINTS:]
if len(self.current_data) > MAX_POINTS:
self.current_data = self.current_data[-MAX_POINTS:]
# Update temperature plot
self.temp_plot.clear()
self.temp_plot.plot(self.temperature_data, pen='r')
# Update current output plot
self.current_plot.clear()
self.current_plot.plot(self.current_data, pen='b')
self.scpi.write(f'CURR {current_output}')
def closeEvent(self, event):
# Stop the PID thread when the window is closed
self.stop_pid()
self.kill_pid()
self.scpi.write('OUTP OFF')
self.scpi.write('SYST:LOC')
event.accept()
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
ex = Expt()
ex.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())

Testing new power supply E36155A
ipython3
jithin@jithin-Victus:/etc/udev/rules.d$ ipython3
Python 3.12.3 (main, Aug 14 2025, 17:47:21) [GCC 13.3.0]
Type 'copyright', 'credits' or 'license' for more information
IPython 8.20.0 -- An enhanced Interactive Python. Type '?' for help.
In [1]: import usbtmc
In [2]: scpi = usbtmc.Instrument(0x2a8d, 0x5902)
In [3]: scpi.ask('*IDN?')
Out[3]: 'Keysight Technologies,E36155A,MY63001609,1.1.15-1.0.1-1.21'
In [4]:
